Composting is a fundamental practice for sustainable gardening and waste reduction. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step overview of the composting process, from initial collection and preparation to the final application of the finished compost.
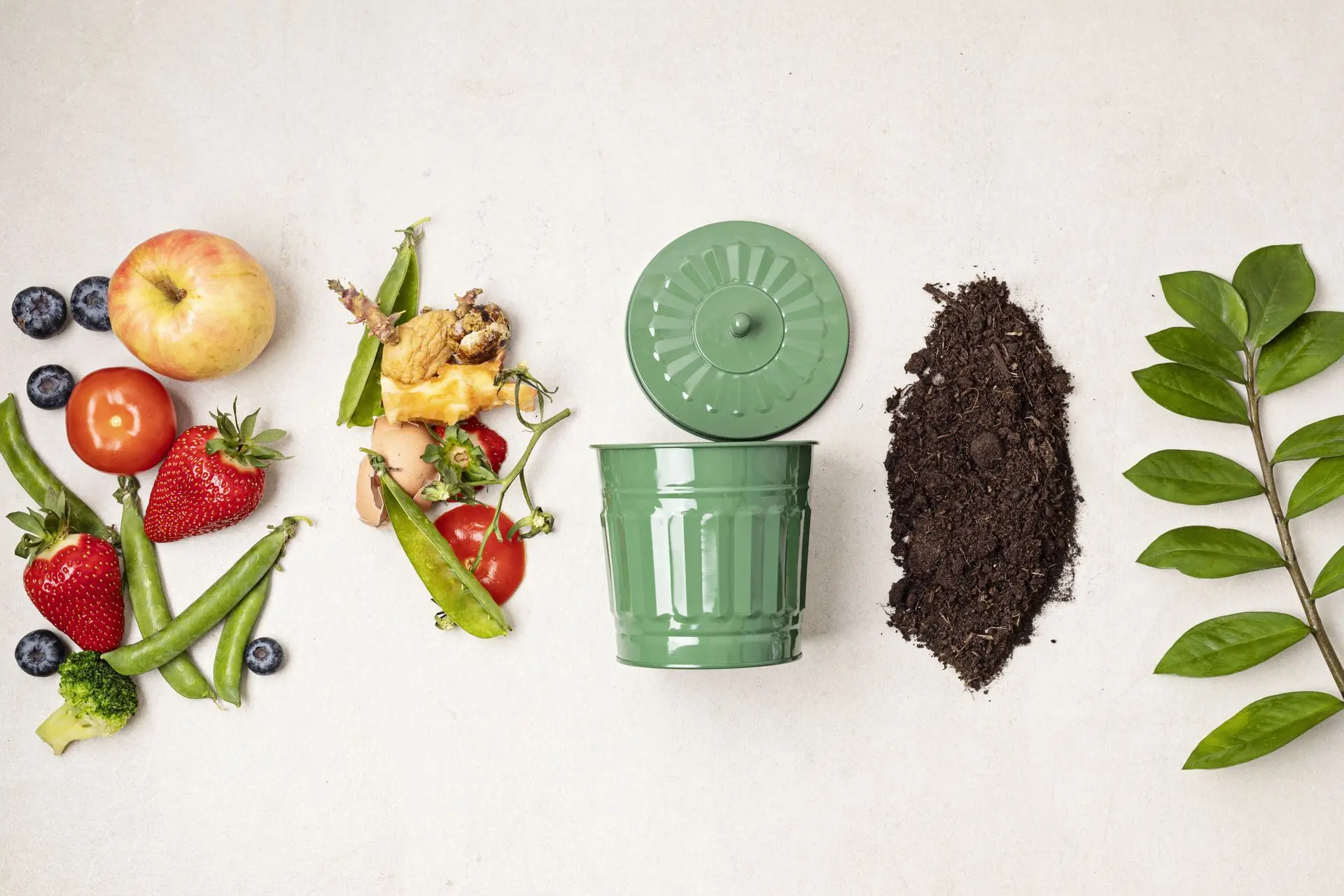

- Collection of Organic Material: Gather kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials. Maintain a balanced mix of green (nitrogen-rich) and brown (carbon-rich) materials.
- Shredding and Layering: Chop or shred larger materials to speed up decomposition. Layer green and brown materials to maintain a proper carbon-to-nitrogen ratio.
- Aeration and Moisture Control: Turn the pile regularly to provide oxygen and prevent anaerobic conditions. Keep the compost moist but not waterlogged.
- Decomposition and Heat Generation: Microorganisms break down organic matter, generating heat and promoting efficient composting.
- Curing and Maturation: As microbial activity slows, the compost stabilizes, transforming into dark, crumbly humus.
- Application to Soil: Once fully decomposed, the compost can be used to enrich garden beds, improve soil structure, and enhance plant growth.